Profiling Guide¶
To maximize the performance of vLLM RBLN, it is essential to perform low-level profiling that allows for an in-depth analysis of RBLN NPU behavior, in addition to monitoring standard metrics such as TTFT (Time To First Token) and TPOT (Time Per Output Token).
This document provides profiling guides for two types: PyTorch-Level Profiler and RBLN Profiler.
1. PyTorch-Level Profiler¶
This method uses the PyTorch Profiler to measure performance at the operation level. It allows for the analysis of kernel execution times and computational bottlenecks. vLLM RBLN supports the same interface as the official vLLM Profiling guide.
1.1 Environment Setup¶
You must set the VLLM_TORCH_PROFILER_DIR environment variable to specify the directory where the profiling results (traces) will be saved.
1.2 Offline Inference Profiling¶
For offline inference using Python scripts, use the start_profile() and stop_profile() methods to wrap the section you wish to measure.
1.3 Online Inference Profiling¶
For online inference via the API server, specific endpoints are called to control profiling.
1. Call the /start_profile endpoint to begin profiling.
2. Send the actual inference request (e.g., /v1/chat/completions).
3. Call the /stop_profile endpoint to stop profiling and save the results.
1.4 Additional Options¶
For more detailed analysis, you can configure the following additional environment variables:
VLLM_TORCH_PROFILER_RECORD_SHAPES: Records tensor shape information.VLLM_TORCH_PROFILER_WITH_PROFILE_MEMORY: Profiles memory usage as well.VLLM_TORCH_PROFILER_WITH_STACK: Records source code stack traces.VLLM_TORCH_PROFILER_WITH_FLOPS: Estimates and records FLOPS (floating-point operations per second).
1.5 Visualizing Profiling Results¶
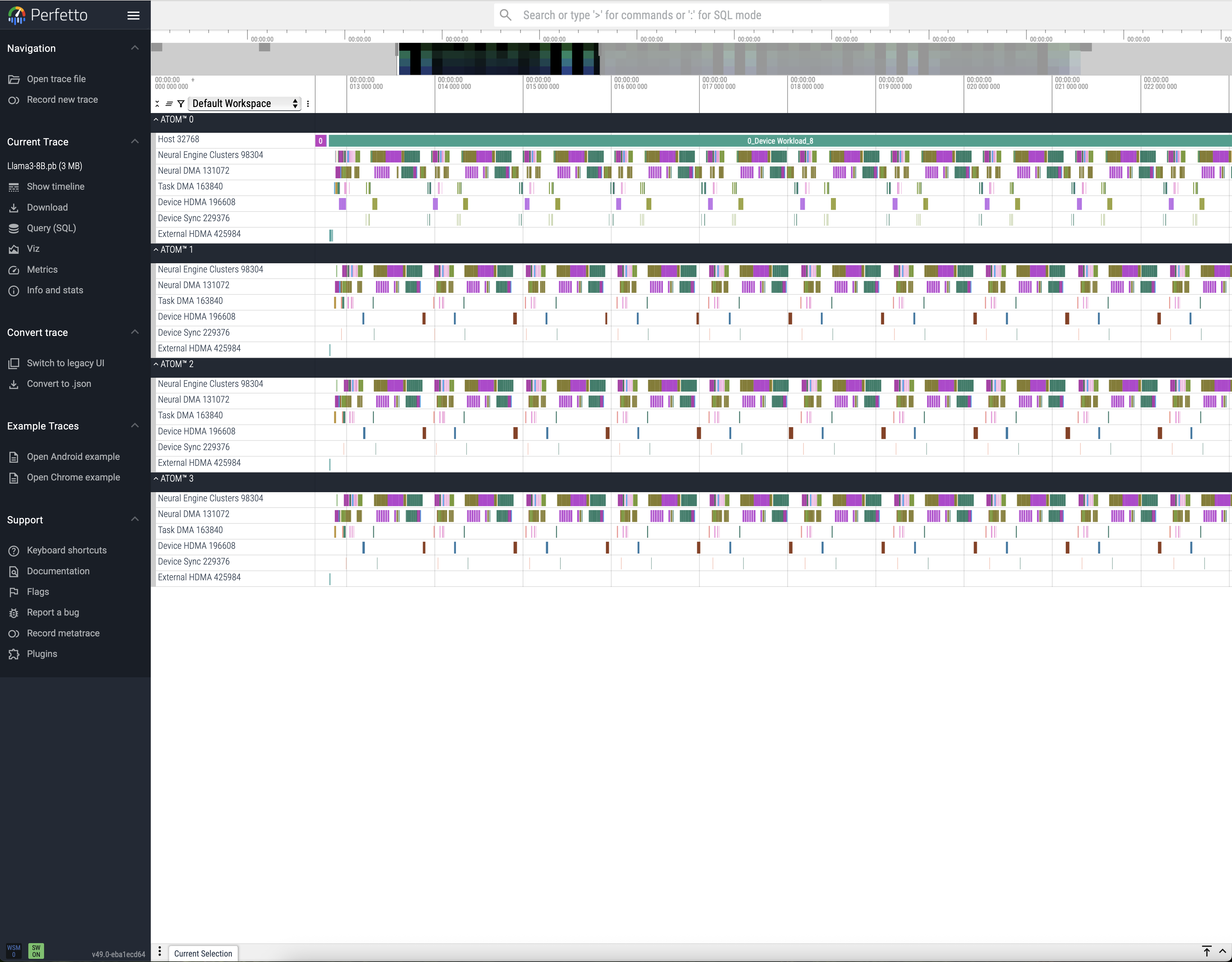
The generated profiling trace files can be visualized using the Perfetto UI.
2. RBLN Profiler¶
The RBLN Profiler is a software tool designed for in-depth performance analysis of workloads running on RBLN NPUs. For more details about RBLN Profiler, please refer to RBLN Profiler
2.1 Constraints and Configuration¶
In the vLLM RBLN environment, profiling with the RBLN Profiler is supported only when the multiprocessing configuration is disabled. Support for profiling with multiprocessing enabled will be included in an upcoming release.
Set the environment variables as shown below and run vLLM to generate profiling results.
RBLN_PROFILER=1: Enables the RBLN Query Profiler.VLLM_ENABLE_V1_MULTIPROCESSING=0: Disables multiprocessing.
2.2 Visualizing Profiling Results¶
The resulting profiling trace files can also be visualized using the Perfetto UI. For more details on trace analysis, please refer to the Perfetto Analysis Guide.