PyTorch RBLN: A PyTorch extension for RBLN NPU¶
Warning
PyTorch RBLN is in beta and subject to change.
PyTorch RBLN(torch-rbln) is a PyTorch extension that allows natural use of the computing power of Rebellions NPU within PyTorch. By implementing eager mode, which operates in a ‘define-by-run’ fashion, it provides essential user experience across the entire lifecycle of model development, deployment, and serving in the PyTorch ecosystem. It is also convenient for various debugging scenarios.
We expect that PyTorch RBLN, with its ability to use the same interface as GPUs or CPUs, will provide a seamless experience for developers and customers who want to utilize Rebellions NPU in PyTorch.
How to install¶
You need an RBLN Portal account to install torch-rbln. To install the latest release via pip:
For details on the latest version and changes, refer to the release notes.
Note
torch-rbln uses out-of-tree extension. Therefore, installing torch-rbln will automatically pull in torch as a dependency.
Design Overview¶
When you execute PyTorch ops like torch.add or torch.mul, they are bound to PyTorch ATen operators like aten::add or aten::mul inside PyTorch. By using the dispatcher, those ATen operations are linked to the target-specific implemenation in various backends like CPU, CUDA and XLA. For this, PyTorch dispatcher mainly uses the device attributes of the input tensors to find which backend serves the operation. Among the backends in PyTorch, there is PrivateUse1 dispatch key which is used by Out-of-Tree (OOT) extension for supporting various devices in PyTorch. PyTorch RBLN uses OOT to register RBLN device specific runtime and op implementation in PyTorch. Therefore, if you define input tensors with rbln device attribute and apply an operator to the tensors, it is dispatched to RBLN op implementation through PrivateUse1 dispatch key. The op implementation is mainly provided by torch.compile, which is the PyTorch interface to RBLN compiler for creating and running executable for RBLN device.
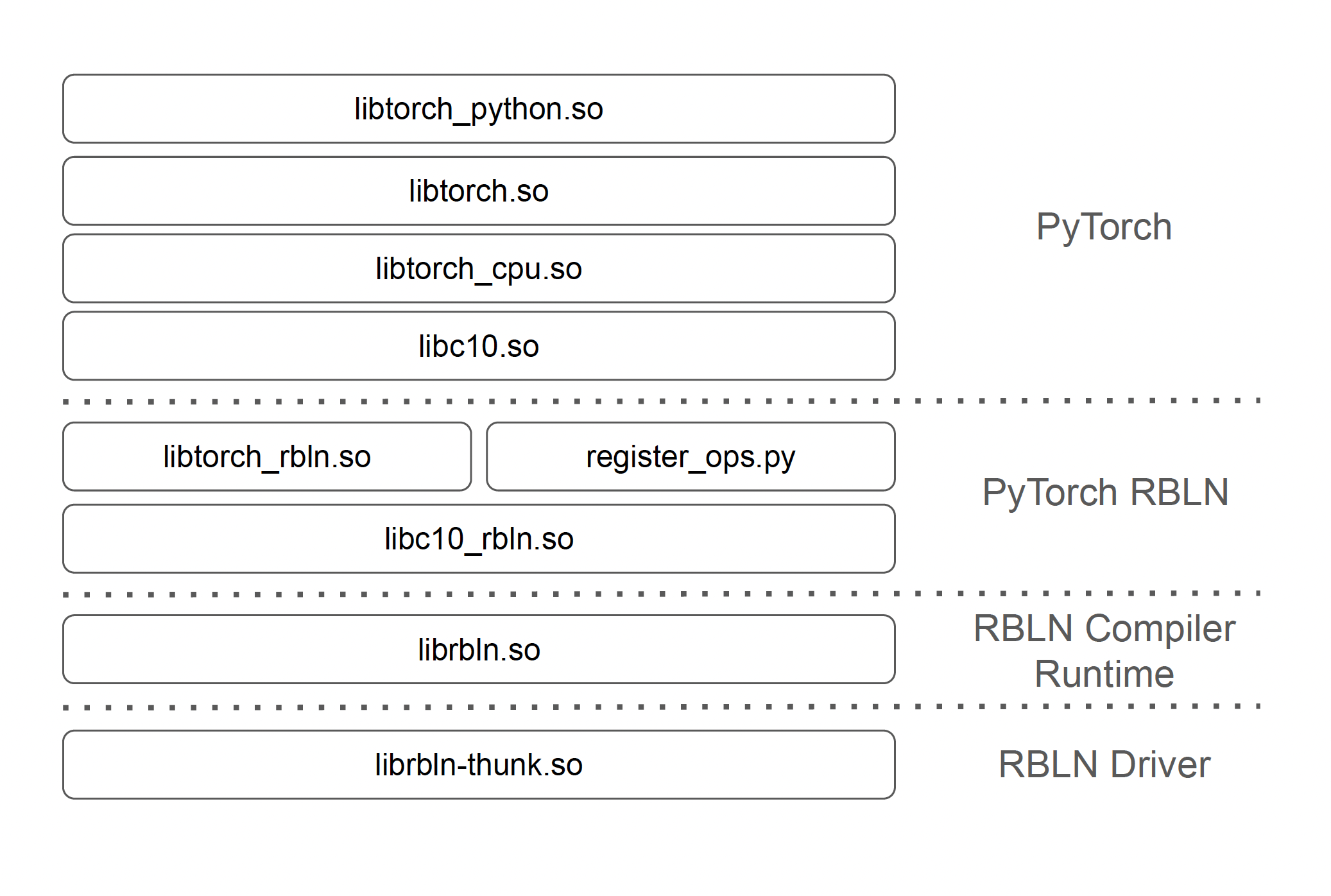
PyTorch RBLN components¶
PyTorch RBLN consists of the following four components: PyTorch, torch-rbln, RBLN Compiler & Runtime, and RBLN Driver.
- PyTorch (
torch)libtorch_python.so: Interface between Python and PyTorch C++ backendlibtorch.so: Main library of PyTorch, providing PyTorch C++ APIslibtorch_cpu.so: LibTorch backend library for CPUlibc10.so: Library for low level PyTorch utilities and basic structure- Tensor management, device abstraction, memory allocation etc.
- PyTorch RBLN (
torch-rbln)libtorch_rbln.so: ATen op C++ library (copy, resize utilizing RBLN Runtime API)register_ops.py: Python op implementations for Rebellions NPU (Usingtorch.compile)libc10_rbln.so: PyTorch runtime component library based onlibc10.so
- RBLN Compiler (
rebel-compiler)librbln.so: Rebellions Compiler and Runtime Library
- RBLN Driver
librbln-thunk.so: Rebellions NPU device driver
Supported Ops¶
You can refer to the list of supported operations in here. The number of supported operations covered by the PyTorch RBLN will continuously expand as the RBLN SDK is updated.
Tutorials¶
To help users get started with PyTorch RBLN, we have created multiple comprehensive tutorials demonstrating its capabilities:
- Basic: how to use PyTorch RBLN with PyTorch.
- Advanced: running
transformersmodel